Exploring the Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map – Unveiling Global Wonders
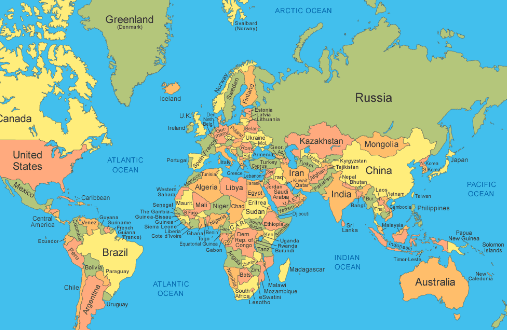
The world map is more than just a visual representation of the Earth. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map It is a gateway to exploring diverse cultures, natural wonders, and historical landmarks. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map Whether you’re a travel enthusiast, a student of geography, or someone curious about the world, the world map is an essential tool. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of the world map, its historical evolution, and how it continues to shape our understanding of the planet today.

The Evolution of the World Map
The concept of mapping the world has been around for millennia. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map From ancient civilizations like the Greeks, who used basic cartography techniques, to modern times where satellite technology offers precise and detailed maps, the world map has evolved dramatically.
- Ancient World Maps: Early maps were often based on myths and religious beliefs. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map For instance, the Babylonian World Map, one of the oldest known maps, depicted the world as a flat disk surrounded by water.
- Medieval Maps: During the Middle Ages, maps were highly symbolic. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map The famous Mappa Mundi placed Jerusalem at the center of the world, reflecting the Christian worldview.
- The Age of Exploration: With the rise of global exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries, the world map started to take on a more accurate form. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama expanded the European understanding of the globe.
- Modern World Maps: Today, world maps are created using advanced technology, offering precise measurements of landmasses, oceans, and even the topography of the Earth.
Why the World Map Matters Today
The world map is not just a tool for navigation; it serves various purposes:
- Educational Value: Maps help students and individuals learn about different countries, continents, and geographic features. Understanding the world’s layout enhances geographical literacy.
- Cultural Awareness: By studying the world map, one can gain insight into how diverse regions of the world are interconnected through trade, history, and migration.
- Travel Planning: For avid travelers, the world map is an invaluable tool. It helps in plotting routes, understanding distances, and identifying must-see destinations.
Key Features of a World Map
- Political Boundaries: One of the primary functions of a world map is to show the boundaries of countries and territories. This helps in understanding international relations and geopolitics.
- Physical Features: A detailed world map includes mountains, rivers, deserts, and other geographical features, providing a deeper understanding of the Earth’s physical structure.
- Scale and Projections: Different maps use various projections, such as the Mercator projection or the Robinson projection. Each has its advantages and drawbacks, especially in terms of distorting the sizes of landmasses.
- Legends and Symbols: A good map uses a legend to explain symbols, such as those representing cities, rivers, or mountains, making it easier to interpret the map’s data.
The Different Types of World Maps
Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map come in various formats and styles, each designed for specific uses. Understanding these types can enhance how you utilize maps for learning, planning, or exploration.
- Political Maps: These are the most commonly recognized types of world maps. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map They highlight national borders, major cities, and capitals. Political maps help you understand the layout of countries and territories in relation to one another. These maps are particularly useful for students learning geography and for individuals interested in global politics.
- Physical Maps: Physical maps depict natural features such as mountains, rivers, and deserts. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map These maps often use color gradients to represent elevation, offering a clearer understanding of the Earth’s terrain. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map Physical maps are ideal for those studying the natural world or planning outdoor activities like hiking and adventure travel.
- Climate Maps: Climate maps focus on the different climate zones of the world, showing patterns of temperature, rainfall, and other meteorological data. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map These maps are essential for understanding global weather patterns, agriculture, and the impact of climate change on different regions.
- Topographic Maps: A topographic map goes beyond showing general features by illustrating the contours and elevations of the Earth’s surface in great detail. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map Used mostly for land surveying, construction, and outdoor expeditions, topographic maps help in understanding the physical landscape at a granular level.
- Thematic Maps: These maps are designed to represent specific themes or topics. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map For instance, a world population density map, a map of languages spoken, or one that charts economic indicators can be classified as thematic maps. These maps are widely used in academic research, business analysis, and policy-making to understand various global trends.
How to Use a World Map Effectively
While world maps are visually stunning, their true value lies in how you interpret the data they present. Here are a few tips to get the most out of your world map:
- Understand the Scale: Most world maps use a scale to represent real-world distances. Familiarizing yourself with the map’s scale will help you estimate distances between countries, cities, or geographical features accurately.
- Know the Map Projection: Every map distorts the Earth’s surface to some degree because a spherical planet cannot be perfectly represented on a flat map. For example, the Mercator projection is commonly used but tends to exaggerate the size of areas closer to the poles. If accurate area representation is crucial, choose a map with an equal-area projection, like the Peters projection.
- Study the Legend: The legend, or key, is vital for understanding what various symbols, colors, and lines on a map represent. Take time to familiarize yourself with the legend to ensure you’re interpreting the map’s data correctly.
- Use Online Tools: With modern technology, interactive world maps like Google Earth offer a dynamic experience. You can zoom in to explore specific regions, track your movements using GPS, and switch between different types of maps, such as satellite views and terrain maps.
Fascinating Facts About World Maps
- Greenland vs. Africa: Many people believe Greenland is nearly the same size as Africa due to the distortions of the Mercator projection. In reality, Africa is about 14 times larger than Greenland.
- The Oldest Surviving World Map: The oldest known world map is the Imago Mundi, created around the 6th century BCE by the Babylonians. It shows the world as a flat disk, surrounded by a circular river representing the ocean.
- The Upside-Down World Map: While most maps place the Northern Hemisphere at the top, this is entirely a matter of perspective. In fact, several mapmakers have produced “upside-down” world maps with the Southern Hemisphere on top, challenging our conventional views of the world.
- Pangea on the Map: Scientists believe that around 300 million years ago, all the continents were joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea. Some world maps attempt to show what the Earth would have looked like before continental drift split the landmasses apart.
World Maps in the Digital Age
The digital revolution has transformed how we use and interact with world maps. Labeled:v-xzjijklp4= World Map Today, tools like Google Maps, Google Earth, and mapping apps offer unprecedented access to geographic data. This shift has revolutionized navigation, making it easier to travel, explore new places, and even visualize remote regions.
- Real-Time Updates: Online maps update in real-time, providing accurate information on traffic, road closures, and even natural disasters. This level of detail makes digital maps an indispensable resource for travelers and commuters.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Maps: Some mobile apps now use augmented reality to enhance navigation. By combining digital data with real-world views, AR maps allow users to navigate complex cities, locate landmarks, and explore regions in more engaging ways.
- 3D Mapping: Digital mapping has advanced to the point where users can view the world in three dimensions. This is particularly useful for understanding the topography of regions like mountain ranges, valleys, and coastlines.
- Environmental Monitoring: Digital maps are now used to monitor environmental changes. From tracking deforestation in the Amazon rainforest to observing the melting of polar ice caps, these maps provide critical data for scientists and policymakers concerned with environmental conservation.
Conclusion
The world map remains a vital resource in the modern world, helping individuals navigate and understand the complexities of global geography. Whether for travel, education, or simply exploring new horizons from the comfort of home, the world map is a constant reminder of the vast and interconnected world we live in.